 Indica Sativa
What is Cannabis?
Indica Sativa
What is Cannabis?
Cannabis is from the hemp family. Hemp has been used for centuries for industrial purposes like rope, fabric, paper, clothing manufacturing and this product has very little of the chemicals that produce mind altering effects. There are two main strains of cannabis that grow naturally. There are also other strains of the cannabis plant that grow in different parts of the world. Cannabis Sativa is a tall plant with slimmer and pointy leaves. Cannabis Indica is a shorter, stockier plant with broader leaves.
What is IN Cannabis?There are around 400 chemicals in the cannabis plant. Many of these chemicals exist nowhere else other than in cannabis. It's the chemicals known as cannabinoids that give the plants its mind altering effects. There are at least 66 different cannabinoids. The main cannabinoids in cannabis are:
- THC (Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) is the more commonly known.
- CBD (Cannabidiol). Both are in all cannabis plants to a degree.
- Cannabis Sativa generally has more THC, while Cannabis Indica has more CBD.
- CBD alone does not seem to be intoxicating, but it appears to modify the euphoric effect of THC and adds a sedative quality.
Herbal cannabis is grown outdoors or indoors often with artificial lights and nutrients or hydroponically. Hydroponics is growing a plant indoors in water. Its leaves and flowers are cultivated and dried. The leaves have less THC, typically 0.5% - 4%. The flowering heads have 3-4 times this concentration. Premium prices are paid for intact flowering buds. THC contents are increased by preventing pollination of female plants by male plants leading to the development of extensive flowering tops. Commercial seed developers have developed a number of varieties of plant such as "Skunk", and "Northern Lights" suited for indoor growth. The cannabinoids level of these plants varies. One striking development is the potency of Skunk (up to 80% of the market), now averaging 16% THC much higher than the average THC in the herbal cannabis of the 60s and 70s. Old cannabis contained an anti-psychotic CBD (cannabidiol) but it is virtually absent in skunk, further increasing the potency and fuelling the increase in psychiatric problems. Brain scans have shown reduced volume in some areas from use of skunk as compared to the milder strains.
ResinDifferent names for the type of cannabis resin usually come from what country it is from. Lebanon, Nepal, Afghanistan are some of the sources of cannabis resin.
Resin is made by separating the sticky resin from the buds and leaves, drying it and forming it into blocks. Different countries have different methods for doing this. Whatever the method, it leaves the potential for other material to be added to increase profits.
OilCannabis oil is the concentrated, distilled form of the plant with all the plant material stripped. Cannabis oil can have the two primary ingredients: The high-inducing THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and cannabidiol (CBD) oil brands currently marketed for medicinal uses contain CBD but both ingredients are being explored for their medicinal potential.
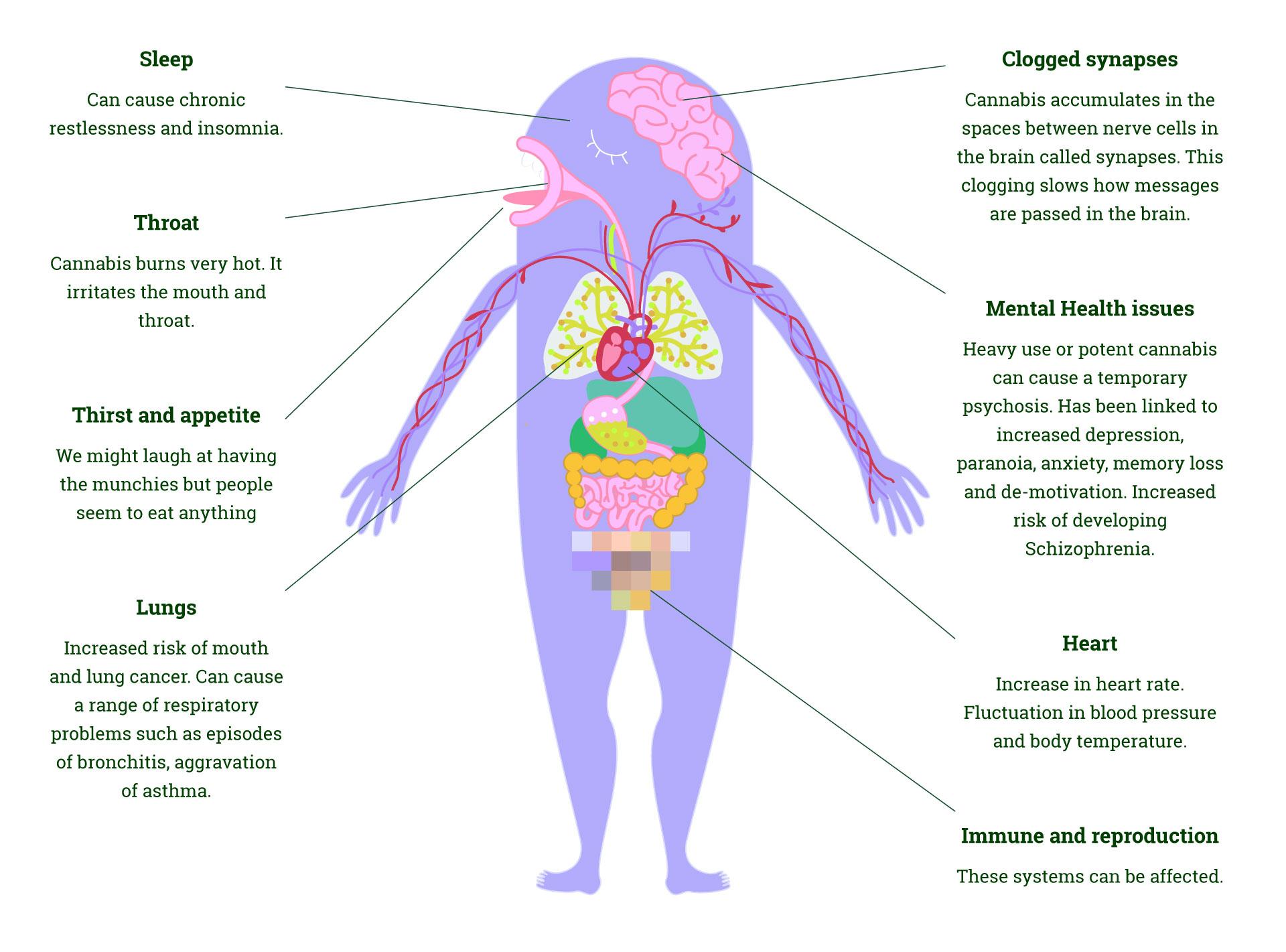
When cannabis is smoked, it is absorbed through the lungs and into the bloodstream. It is detected in the blood within one or two minutes of inhaling. It is then distributed throughout the body reaching the brain and also concentrated in the body's fat stores. Cannabis can still be detected days, even weeks after use as it is stored in fat cells. The THC connects to specific cannabinoids receptors in the brain and influences how those nerve cells work. The cannabinoids receptors are found in parts of the brain which control:
 If you have used cannabis, you know the range of different effects at different times.
If you have used cannabis, you know the range of different effects at different times.
Some of these can seem contradictory; relaxed, calm, anxious, restless, quiet, talkative, giggly, subdued, sleepy, animated, and distorted perception. The effects of different drugs are caused by the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. While most drugs affect 1-3 neurotransmitters, cannabis affects at least half a dozen, including serotonin, dopamine and endorphins. This explains why cannabis has such a wide range of effects on the mind: tripping, stimulating, pain killing, relaxing, etc. At low and moderate levels of THC, the user may experience enhanced appreciation of sound, colour and tactile stimulation. At higher levels mild hallucinations can happen. There are also a range of side effects: dryness of the mouth, reddening of the eyes, cough, husky voice, intense desire to eat. Users can also have a range of less pleasant effects: anxiety, paranoia, dizziness, nausea, disorientation."Whities", suddenly feeling dizzy, sick or weak are often caused by hypotension or low blood pressure but can also be caused by other factors like not eating or drinking alcohol.
The effects of taking cannabis can be highly variable and subjective. It can be influenced by:
- Amount taken
- Strength and type of the cannabis
- Method of use (smoked or eaten)
- Mental state of the user
- Other substances used, like alcohol
- The setting of use
- The expectations and experience of the user
The strength of cannabis will change under certain circumstances.
For example, cannabis does not stay fresh and exposure to air reduces the THC level. As THC breaks down (a process known as oxidation) the THC is replaced by CBN (Cannabinol) which leaves the user feeling more messed up than stoned. This can also happen when processing the herbal cannabis to resin.
People can have very different reactions to cannabis use. How much effect cannabis has on anyone can depend on how much you've used, how often, how long you've been using and pre-existing medical or psychiatric conditions. This is by no means an exhaustive list as research continues to build on what we know of its impact on people.
Even one-off use of cannabis can cause a sense of panic and increased anxiety. Experts are closely examining if cannabis increases the risk of serious mental health difficulties.
What is known so far: SchizophreniaDoes it cause schizophrenia? Available evidence suggests that people who use cannabis in their teens have an increased risk of developing schizophrenia when compared to non-cannabis users.
Cannabis (THC) increases the amount of the dopamine in the brain. When psychotic or suffering from schizophrenia people have an excess of dopamine. Cannabis users double the chances of developing this condition. Schizophrenia is a chronic, often lifetime condition.
It was reported that users of skunk increase their risk of psychotic disorder three-fold compared to those who have never used, daily skunk users - five-fold (Murray et al, 2015).
Using it to manage symptomsSome people with mental illness use cannabis to relieve their symptoms. It can actually make the condition worse and more difficult to manage.
DepressionPeople who use cannabis are also more likely than others to experience episodes of depression.
Psychotic episodesAfter a session of heavy cannabis use, people can experience a short term psychotic episode that can last from several hours to two or three days. In these episodes there is a loss of contact with reality, disordered thought, paranoia and sometimes hallucinations. Such an episode is caused by the direct effects of cannabis on the brain.
Brain damageIn the last few years, brain scans have found brain damage in cannabis users particularly using skunk. The volume of gray matter (brain cell bodies) has been reduced in some areas rich in cannabis receptors. These include the hippocampus (learning), amygdala (emotions), anterior cingulate (motivation) and prefrontal cortex (intelligence, problem solving and decision-making). Having a family history of mental illness increases the likelihood of experiencing negative mental health effects when cannabis is used regularly. Is there a history of mental health problems somewhere in your family?
There are no labels you can read are there? When sold commercially as in the coffee shops in the Netherlands, you can choose off a menu. When bought off the streets in Ireland it is often pot luck. In the vast majority of cases, you will have no idea what you are buying.
What we know (not an exhaustive list by any means):
- High strength weed is more dangerous to your mental health.
- Some resins have things added such as bees wax, boot polish, animal excrement, turpentine, ground coffee, milk powder, pine resin, barbiturates, ketamine, aspirin, glues and dyes.
- Damp can cause mould on cannabis, which can be dangerous to the user, when it is smoked or eaten. Fertilisers, pesticides and hormones which are used to increase yield can cause headaches and other side effects.
- Grit weed, where fibre-glass balls are sprayed onto herbal cannabis to increase its weight, can cause serious damage to the users' lungs. It is really hard to detect, but if you rub the bud with a wet finger then put that finger into your mouth you may feel the glass balls grind in your teeth.
- Synthetic cannabinoids may be sprayed onto weed with low natural THC to create the impression that it is more potent. Synthetic cannabinoids seem to cause more mental health problems than natural THC.
- If you are HIV+ or have cancer there may be a risk from fungi or bacteria in cannabis. The best way to combat this is to place your cannabis in an oven heated to 66-93° C for about 10 minutes to kill the fungi or bacteria.
Researchers have looked at ways of using that reduce the harm for cannabis smokers. Any smoking is harmful to the lungs, throat and heart. How you decide to take cannabis can have an influence on how much harm you do to these areas of the body. While debates do go on as to which is more harmful, any effort to reduce the harm is worth considering if you decide to keep using.
InhalingAvoid holding smoke in your lungs. You won't get more stoned but you will increase the amount of toxins in your lungs. Most of the THC is absorbed in seconds so holding the smoke in only increases the absorption of nasty chemicals into your lungs.
Seeds and stemsThrow away the seeds and stems when smoking herbal cannabis as they contain little to no THC and can be harsh on the throat.
Use of tobaccoAvoid mixing cannabis with tobacco. Tobacco is addictive and exposes you to more tar and other carcinogens. The lungs are just not made to take in all that hot, toxic smoke. Smokers who mix their cannabis with tobacco find they are smoking more than they intend to because of the addiction to nicotine.
Important things that need to be saidNever use cannabis and drive. You may think you are capable, but it lowers your reaction times and puts you and others at serious risk. Avoid mixing drugs including alcohol. It makes things more unpredictable. Using any drug while pregnant can harm the unborn baby
Different ways of using cannabis: BongsA bong or water pipe is seen as less harmful because the water inside the bong cools cannabis which burns very hot. The water in the bong also removes some of the heavy tar elements. Do not use plastic bottles, rubber hose or plastic stems, or aluminium as these give off harmful fumes when hot.
PipesIf you use a pipe choose one made of glass or stainless steel or brass - wooden and plastic pipes can give off noxious fumes.
FiltersIf you are using a piece of cardboard as a 'tip' or 'roach' use unprinted card as the print emits toxic fumes.
VaporizersUsing a vaporizer to use cannabis stops you taking in smoke. There are some who believe this is the least harmful way of using cannabis.
Eating CannabisEating Cannabis may reduce some risk but increase others. Some people eat cannabis by mixing it with food, or adding it to drinks. Herbal cannabis has little or no effect unless cooked in the correct way. The thinking behind this is that it reduces damage to the lungs through smoking. There is a down side though. The effects from eating cannabis last longer. When cannabis is eaten it can take an hour or two to feel the effects, so avoid eating more in one session. Avoid using stronger cannabis if you are not used to it. Start with smaller test amounts since a gram can be like a mushroom or LSD trip and leave you high longer that you anticipated. Cannabis bought on the street may also have chemicals in it that just are not good for you. NEVER eat cannabis without cooking it.
Synthetic cannabinoids and cannabis are very different drugsSynthetic cannabinoids are included in a group of drugs called "new psychoactive substances" (NPS). NPS are unregulated psychoactive (mindaltering) substances that have become available on the market and are intended to copy the effects of illegal drugs. These were previously known as "legal Highs". The law changed in 2016 when any drug that mimics an illegal drug became illegal. There is controversy about calling drugs like Spice and K2 synthetic cannabis. "Synthetic marijuana" is just not accurate according to experts. The term synthetic does not apply to the plant but rather to the chemical that the plant contains (tetrahydrocannabinol). The term synthetic cannabinoid is more appropriate. They are really quite different, and the effects are much more unpredictable.
It's dangerous, and there is no quality control in what you are getting.Research on the safety of synthetic cannabinoids is now becoming available.Synthetic cannabinoid intoxication is associated with acute psychosis. It may trigger a chronic (long-term) psychotic disorder among vulnerable individuals such as those with a family history of mental illness. The term synthetic does not apply to the plant but rather to the chemical that the plant contains. The term synthetic cannabinoid is more appropriate. It is stated to be more toxic to the brain and more addictive than real cannabis. The European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) has issued an alert on 36 serious adverse events (13 deaths and 23 nonfatal intoxications) across Europe associated with the synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA. These occurred between September 2014 and July 2015. While you could use what is in this booklet to help you change your use of Synthetic cannabinoids there are things in the booklet that won't work. The CUDIT is for cannabis and not for Synthetic cannabinoids. The bottom line: Be careful with these drugs. They cause people a lot of problems. A closer look at cannabis Types of cannabis How cannabis works in the brain and body Cannabis use and mental health How do you know what you're getting? Is one method safer than another? The law Whether











